Why So Volatile?
Everyone knows that crypto prices are volatile. But why?
Exchange, Software, Human & Government volatility triggers are the triggers that influence the movement of the Information Curve (i.e., price movements). In this post, I will go into detail about how each volatility trigger causes crypto asset prices to have volatile downward and upward swings. All volatility triggers have both positive and negative impacts on crypto-asset prices.
4 Volatility Triggers Categories:
- Exchange Volatility Triggers
- Forced stoppage - When an exchange is unable to support trading demand or supply, they will limit transaction volume.
- Transactions fee - Crypto-exchanges use this as their main or even revenue generating
- Withdrawal minimums - They are used to keep crypto-exchanges’ liquidity high and stable
- Software (Blockchain or DAG) Volatility Triggers
- Blockchains’ (or DAGs’) maximum amount of transactions per second-Crypto traders are unable to get their transactions verified and could lose their coins under certain circumstances.
- Transactions fees - Used to incentivize miners to verify transactions for “Proof of Work” consensus Blockchains. In Bitcoin’s case, it was cost prohibitive. Bitcoin fees reached $50+ during it’s Dec. 2017 price peak.
- Hard Forks - The offshoot of an existing crypto-currency and it’s underlying blockchain. For example, Bitcoin Cash is a hard fork of Bitcoin. Most hard forks are done by miners to make more money with a new coin with less mining competition (i.e. they can make higher fees or mine newer coins for profit, quicker)
- Soft Forks - Infrastructural improvements to an existing Blockchain (or DAG) that are backward compatible
- Human Volatility Triggers
- Human errors
- Emotional Trading - A majority of crypto traders trade on pure emotion. When they see “extreme” price movements, they act on it without adequate short & long term investment strategies.
- Misplaced private keys - Private keys can be lost if they are printed out, and you forget where you saved the physical copy of your private keys
- Failure resetting hard wallets - Hard wallets such as the Ledger, should always be reset to factory settings if you purchased a used one. It’s always safer to purchase a new hard wallet directly from the manufacturer.
Bot Trading — Automated put, sell clauses used to minimize losses and maximize trades
- Hacking
- Phishing attacks -Hackers purchase a dummy URL (Hackers purchases Bitcin.org vs Bitcoin.org) setup a fake version of an ICO’s website and ask crypto investors to submit cryptocurrencies to their wallet.
- Phone porting attacks - Hackers steal your mobile phone number and use it to gain access to crypto-assets via mobile apps.
- Human errors
- Government Volatility Triggers
1. Laissez Faire Regulation - Regulation that protects all vested parties from fraud or increases adoption and usage of blockchain and cryptocurrencies.
2. Extreme Regulation - Regulation that hinders blockchain and cryptocurrency adoption.
Examples of Each Crypto Volatility Triggers:
Crypto Exchange Breaker
Positive Price Swing - In December 2017, Binance, Coinbase, Gemini, and other exchanges, either froze new user registrations or had extended periods of delayed KYC processing. This was due to them not being able to efficiently process requests as well as not having proper fraud detection systems in place. This added to the feverish popular sentiment that drove FOMO and caused the crypto market to jump close to $900 Billion market cap. I felt it would be useless to show the same graphs over and over again. Suppressed demand will always produce more FOMO and drive crypto prices up.
On January 7th, the peak crypto market capitalization was $813+ Billion
Negative Price Swing - On Wednesday, December 20th, 2017, Coinbase halted Bitcoin Cash (BCH), a Bitcoin hard-fork. Coinbase was unable to handle the huge trade volume and decided to pause BCH trading.
The BCH popular sentiment dropped by 78% after Coinbase paused BCH trading
At peak price on GDAX (Coinbase), BCH was listed at $8500 which was three times higher than other exchange. On January 8th, 2018, BCH’s price fell by $591.89.
Software (Blockchain or DAG) Volatility Triggers
Positive Price Swing - Coinbase and Bitfinex implemented the Segwit update. Segwit is supposed to lower BTC transaction fees and processing times. For those benefits to be truly realized, 95% of BTC transactions must come from Segwit activated BTC wallets. This has contributed to BTC gaining more dominance, which shows how much of crypto-asset market capitalization is attributed to BTC market cap.
Since, their announcements on February 20th, 2018, BCH price has fallen by 8% or $116.04, and BTC’s dominance has increased to 39% up from 37% as of January 1st, 2018. This means crypto-traders are transacting in BTC more readily.
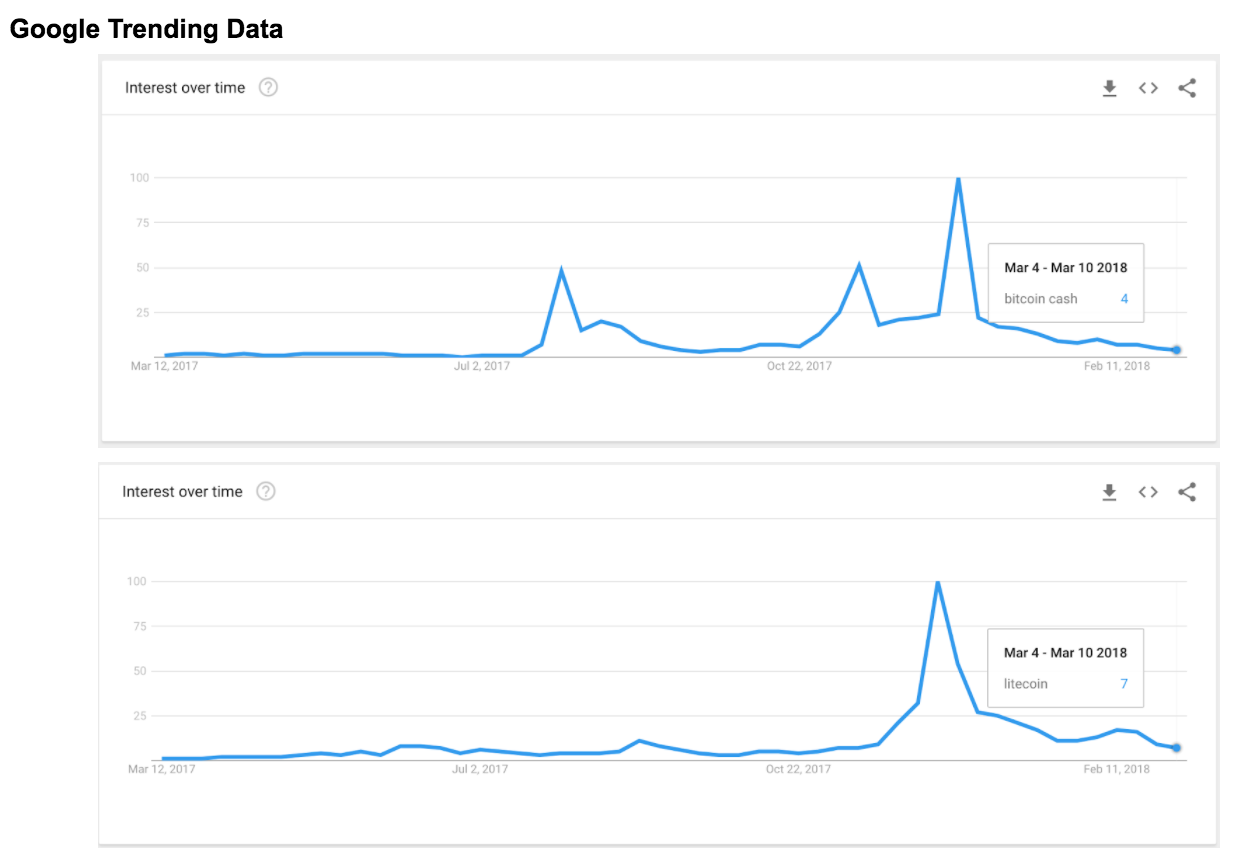
Negative Price Swing - Since, the Coinbase and Bitfinex announcements, BCH price has fallen by 8% or $116.04. BCH was created because the Bitcoin Core group could not agree on the best implementation of faster transactions. This soft fork has the potential to continue lowering the value of BCH as it takes away the main reason to use BCH, cheaper transactions. In the short term, I see it being used less (and becoming cheaper). Both Litecoin (LTC) and BCH were created to allow for cheaper transaction fees. With the Segwit update, from a technical standpoint, it makes them less viable. The drop in their individual domainances rates, shows they are being used for less (fewer or higher value) transactions.
Both LTC and BTC’s popularity as shown on Google Trends has been on a downward spin. On January 1st, 2018, BCH’s dominance was 6.83%, and now it sits at 4.85% dominance. Which is a signal crypto-traders are using it less to move their money.
Human Volatility Triggers
Positive Price Swing - Coincheck was hacked, and hackers stole $650 million worth of NEM. Afterwards, Coincheck contacted NEM developers, and the NEM developers developed a color-coding mechanism for tracking and identifying lost or stolen NEM.
Surprisingly, after looking at the price data, it shows that crypto-investors started to purchase more NEM. I guess that some savvy investors purchased NEM as it’s price dipped, increased “popularity” caused new investors to buy more NEM or lastly, NEM’s newly created tagging system caused the short-term trust to increase a (“positive” swing in sentiment) hence, driving up NEM’s value up momentarily.
Afterward, NEM’s popularity and prices started and continued to decrease in February 2018.
Negative Price Swing - Coincheck, a Japanese crypto exchange, was hacked for $650 million worth of NEM. As a result, Coincheck, froze withdrawals, an exchange breaker, to limit more NEM from being stolen or lost and to limit a “bank run,” and as a result, NEM’s price was $.81 on Friday, January 26th and as of Thursday, February 15th it is $.57.
NEM’s popularity increased after news broke out about Coincheck being hacked. After analyzing the negative price movement, it shows that the increased popularity was “negative” (investors looked down on NEM) causing crypto-investors to sell off or avoid buying NEM. Crypto-exchange hacks rarely involve the underlying crypto-coins’ blockchain or DAG being damaged, however, most crypto-market participants do not understand the underlying Blockchain technology, causing irrational price swings. After February 3rd, 2018, NEM’s popularity decreased down to a 33%.
Government Volatility Triggers
Positive Price Swing - Venezuela launched Petro, the first state-sponsored security token backed by their oil deposits. Venezuela’s president, Nicolas Maduro, announced that $5 Billion worth of Petro had been sold during their pre-sale. The coin has not been listed on any crypto-exchanges, and there is no information about prices on Coinmarketcap.
The popularity of the coin peaked the 3rd week of February-the middle of their pre-sale. This was driven by popular media coverage (outside typical crypto media outlets): BBC, CNBC, Reuters and The Washington Post. I am expecting the Petro to retain at least 50% of it’s pre-sale value and we may even see a 300% - 400% uptick in price, as new ICO coins tend to be “pumped and dumped” by strategic investors.
Negative Price Swing - South Korea’s plan crypto-currency trading, caused the crypto-markets to lose value. It is widely known, South Korea along with Japan and China are the biggest drivers for crypto-asset markets, driving up the value of the entire market.
After the announcement, BTC’s popularity and total crypto asset market cap both fell by almost 50%.
Observations:
Higher BTC dominance is analogous to altcoins becoming bargain buys. Strategic investors are consolidating their profits into BTC.
Lower BTC dominance is analogous to altcoins being better bargain buys. Strategic investors are keeping their altcoins bets in place.
Prediction:
Decentralized exchanges will increase price volatility because more trades will be tracked and triggering more emotional (or reactive) trading. If you have any recommendations on my analysis, feel free to share. I am not a financial advisor, and this is not investment advice.
I would like to thank Kingsley and Blackchain for proofreading this post. If you have any recommendations on my analysis, feel free to share. I am not a financial advisor, and this is not investment advice. If you are interested in learning more about crypto. Subscribe to my newsletter here for latest crypto industry updates.
Donate to help fund further crypto-economic analysis:
BTC: 1LpyW83yTW4jQuDvVLW9H2vWf8SyGu8EqU
ETH: 0x0a164f29A2d08158Cc04Acb35e17Cbe9bFFFA13A
NEO: AcvZKu3gwXkuKU7aeXetBaEUGnTzsJKRv9